Joel is currently receiving treatment for the condition, which includes specific physical therapy (Pic: Instagram/iStock)
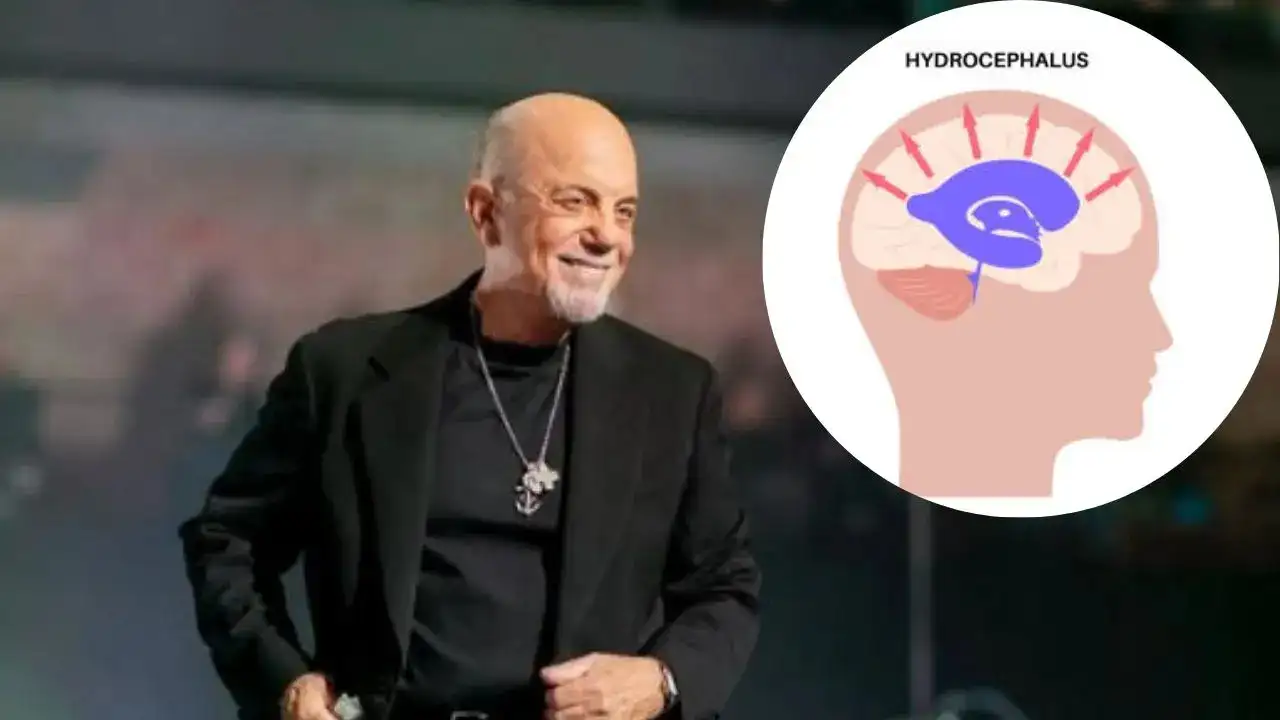
Renowned singer Billy Joel cancelled all his upcoming concerts after he was diagnosed with normal pressure hydrocephalus—a cognitive brain condition. The 76-year-old announced it in a statement shared across his social media accounts. According to Jodel, his condition has been "exacerbated by recent concert performances, leading to problems with hearing, vision, and balance," the statement read.
According to news reports, the "Piano Man” singer is currently receiving treatment for the condition, which includes specific physical therapy, and has been advised to refrain from performing during this recovery period.
What is Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus?
According to experts, normal pressure hydrocephalus is formed when fluid buildup inside or around your brain starts to disrupt your brain function. It affects many brain-related abilities, including thinking and concentrating, memory, movement, and much more. The symptoms of this condition are very similar to those of dementia; however, NPH is sometimes reversible.
Doctors say NPH is most common in people over 65 years old, becoming more and more common the older a person gets. The average age for this condition to start is around 70.
Increasing age is the only factor that makes this condition more likely to happen. The odds of it happening don’t change depending on a person’s ethnicity, race, sex, etc.
Even though it is relatively uncommon, NPH affects around 0.2 per cent of people between the ages of 70 and 80 years and about 5.9 per cent of those over 80. This means it affects about 8.4 million people over the age of 80 across the world. Experts estimate NPH is very rare in people under 65, only affecting about 0.003 per cent of people in that age group.
Signs and symptoms of normal pressure hydrocephalus
According to doctors, the symptoms of NPH start gradually, developing and worsening over the span of three to six months. The three main symptoms are known as Hakim’s triad, which more than 50 per cent of people have. Hakim’s triad includes three types of symptoms:
Gait issues
This happens when you have trouble with walking-related movements, which more than 80-90 per cent of people have. Some of these also resemble movement-related symptoms of Parkinson's disease. You may have issues with:
Lifting your feet
- Your steps becoming shorter and unsteady
- Freezing or walking uncertainly
- Rotating your toes outward as you walk
Urinary incontinence
It happens when you lose control of your bladder, causing you to pee unintentionally. It can lead to peeing, often feeling the urge to pee that’s unusually strong, difficult to control, or both. You may feel the loss of bladder control.
Cognitive difficulties
The third key symptom type of NPH is cognitive difficulties. Which appear as:
- Mental and physical slowness
- Memory issues
- Executive dysfunction
- Emotional changes
What causes Normal Pressure Hydrocephalus?
There are two forms of NPH, and they happen at equal rates, including primary and secondary NPH.
Primary NPH means it does not happen due to a medical condition but for unknown reasons. Experts suspect idiopathic NPH can involve one or more age-related issues with how your body makes, circulates, and reabsorbs CSF. About half of NPH cases are idiopathic.
Secondary NPH happens when another medical condition affects how your body makes, circulates, or reabsorbs CSF. Some examples of conditions that can cause secondary NPH include brain aneurysm, bleeding around your brain, brain tumours, infections, stroke, or traumatic brain injuries.
